あい
今回はPythonを
使って複数の
ヒストグラムを
重ねたり
並べたりします
[PR]※本サイトにはプロモーションが含まれています
ヒストグラム(histogram)とは?
連続データの分布を
視覚的に表現するためのグラフ
縦軸を度数、横軸を各区間に分け
グラフを作ります。

あい
今回は複数のデータから
MatplotlibのFigureと
Axesを利用して
ヒストグラムを作成
並べたり重ねたりします
2つのデータからヒストグラムを作成し重ねる
2つのデータからヒストグラムを作成し重ねる
コードはこちらです
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 日本人成人男性の平均身長に見立てたデータ
man = np.random.normal(170.7 , 6.4, 1000)
# 日本人成人女性の平均身長に見立てたデータ
woman = np.random.normal(158.8,5.8,1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# 男性の身長データのヒストグラムを描画
ax.hist(man, bins=50, color='blue', alpha=0.5, label='Men')
# 女性の身長データのヒストグラムを描画
ax.hist(woman, bins=50, color='red', alpha=0.5, label='Women')
# タイトル
ax.set_title('Japanese height data')
# x軸とy軸にラベルの追加
ax.set_xlabel('Height[cm]')
ax.set_ylabel('Frequency')
# データラベルの追加
plt.legend()
# グリッド線の追加
ax.grid(True)
# Show the plot
plt.show()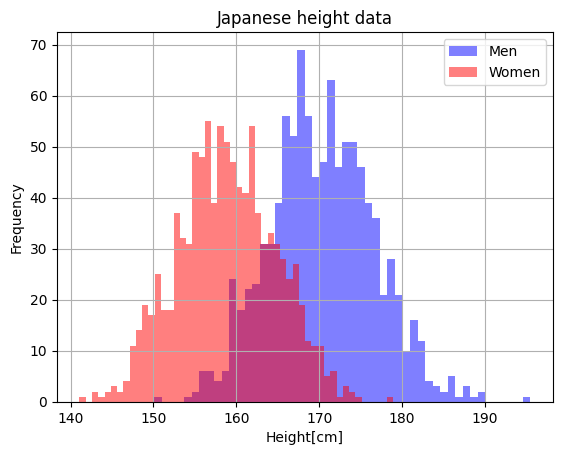

あい
綺麗に重なった~
fig, ax = plt.subplots()figでグラフがかける領域を取得し
axで描写領域内に座標軸を呼び出します

今回は1つの座標軸しか
呼び出していないので
同じところに2回書けばグラフは重なるはずです。
# 男性のヒストグラムを描画
ax.hist(man, bins=50, color='blue', alpha=0.5, label='Men')
# 女性のヒストグラムを描画
ax.hist(woman, bins=50, color='red', alpha=0.5, label='Women')プログラムを確認すると
同じ所に2回書いているのが
確認できますね
最後にax.hist内の
オプションを説明をします
| color | ヒストグラムの色 |
| alpha | 色の濃淡 |
| label | 分布の名前 |
ヒストグラムを並べる
日本人成人男性と女性
の身長データに
アメリカ人成人男性と女性の
データを追加して
ヒストグラムを1つずつ描写し
並べたいと考えています。
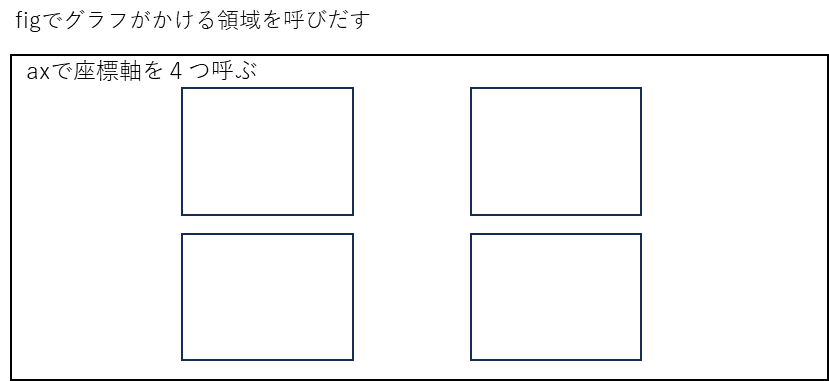
axで座標軸を4つfig内に
呼び出せば並べられると
考えました。
コードはこんな感じです
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 成人の日本人身長に見立てたデータ
man = np.random.normal(170.7 , 6.4, 1000)
woman = np.random.normal(158.8,5.8,1000)
# 成人のアメリカ人の身長に見立てたデータ
A_man = np.random.normal(176.1 , 7.1, 1000)
A_woman = np.random.normal(162 , 7.3, 1000)
# 1行2列のサブプロットを作成
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(10, 8))
# 日本人男性の身長データのヒストグラムを描画
axs[0, 0].hist(man, bins=50, color='blue', alpha=0.5)
axs[0, 0].set_title('Japanese Men Height')
axs[0, 0].set_xlabel('Height [cm]')
axs[0, 0].set_ylabel('Frequency')
axs[0, 0].grid(True)
# 日本人女性の身長データのヒストグラムを描画
axs[0, 1].hist(woman, bins=50, color='red', alpha=0.5)
axs[0, 1].set_title('Japanese Women Height')
axs[0, 1].set_xlabel('Height [cm]')
axs[0, 1].set_ylabel('Frequency')
axs[0, 1].grid(True)
# アメリカ人男性の身長データのヒストグラムを描画
axs[1, 0].hist(A_man, bins=50, color='blue', alpha=0.5)
axs[1, 0].set_title('American Men Height')
axs[1, 0].set_xlabel('Height [cm]')
axs[1, 0].set_ylabel('Frequency')
axs[1, 0].grid(True)
# アメリカ人女性の身長データのヒストグラムを描画
axs[1, 1].hist(A_woman, bins=50, color='red', alpha=0.5)
axs[1, 1].set_title('American Women Height')
axs[1, 1].set_xlabel('Height [cm]')
axs[1, 1].set_ylabel('Frequency')
axs[1, 1].grid(True)
# グラフをタイトに配置
plt.tight_layout()
# グラフを表示
plt.show()出力です
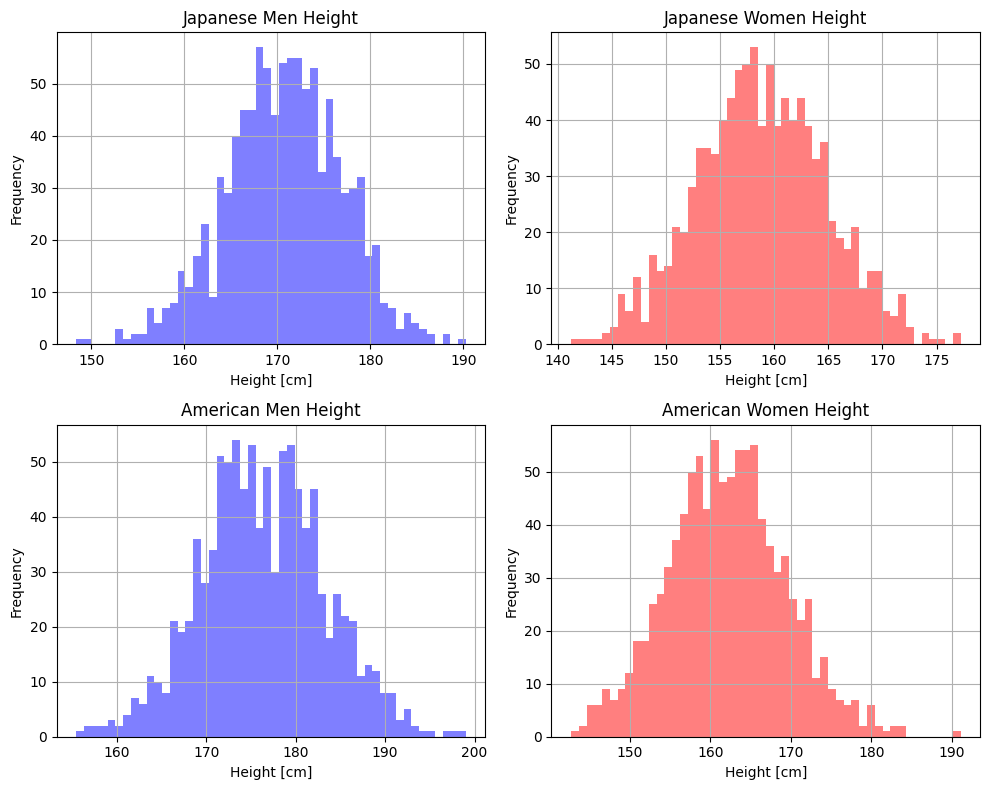
プログラムを見てみます
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(10, 8))このプログラムは
幅10インチ高さ8インチの
2×2のプロットする場所を
作るプログラムです
グラフをプロットする場所は
ax[,]で指定できます
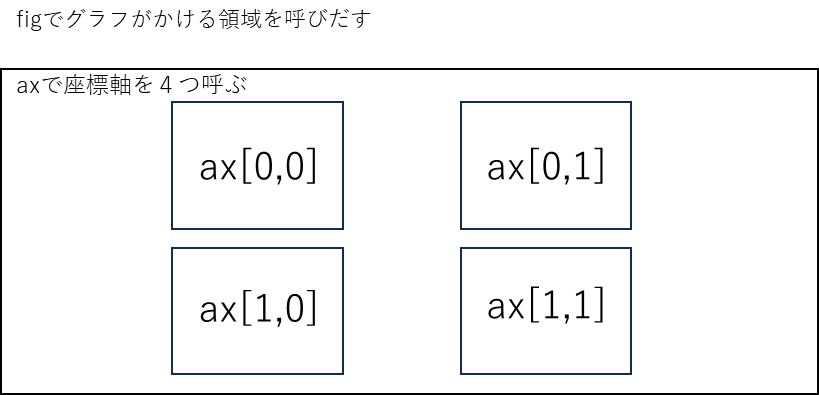
同性同士の身長の分布を重ねる
最後に同性同士の
ヒストグラムは重ねることにします
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 日本人成人の身長に見立てたデータ
man = np.random.normal(170.7 , 6.4, 1000)
woman = np.random.normal(158.8,5.8,1000)
# アメリカ人成人の身長に見立てたデータ
A_man = np.random.normal(176.1 , 7.1, 1000)
A_woman = np.random.normal(162 , 7.3, 1000)
# 1行2列のサブプロットを作成
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(10, 8))
# 日本人男性とアメリカ人男性の身長データのヒストグラムを重ねて描画
axs[0].hist([man, A_man], bins=50, color=['blue', 'green'], alpha=0.5, label=['Japanese Men', 'American Men'], stacked=True)
axs[0].set_title('Height Comparison (Men)')
axs[0].set_xlabel('Height [cm]')
axs[0].set_ylabel('Frequency')
axs[0].legend()
axs[0].grid(True)
# 日本人女性とアメリカ人女性の身長データのヒストグラムを重ねて描画
axs[1].hist([woman, A_woman], bins=50, color=['red', 'orange'], alpha=0.5, label=['Japanese Women', 'American Women'], stacked=True)
axs[1].set_title('Height Comparison (Women)')
axs[1].set_xlabel('Height [cm]')
axs[1].set_ylabel('Frequency')
axs[1].legend()
axs[1].grid(True)
# グラフをタイトに配置
plt.tight_layout()
# グラフを表示
plt.show()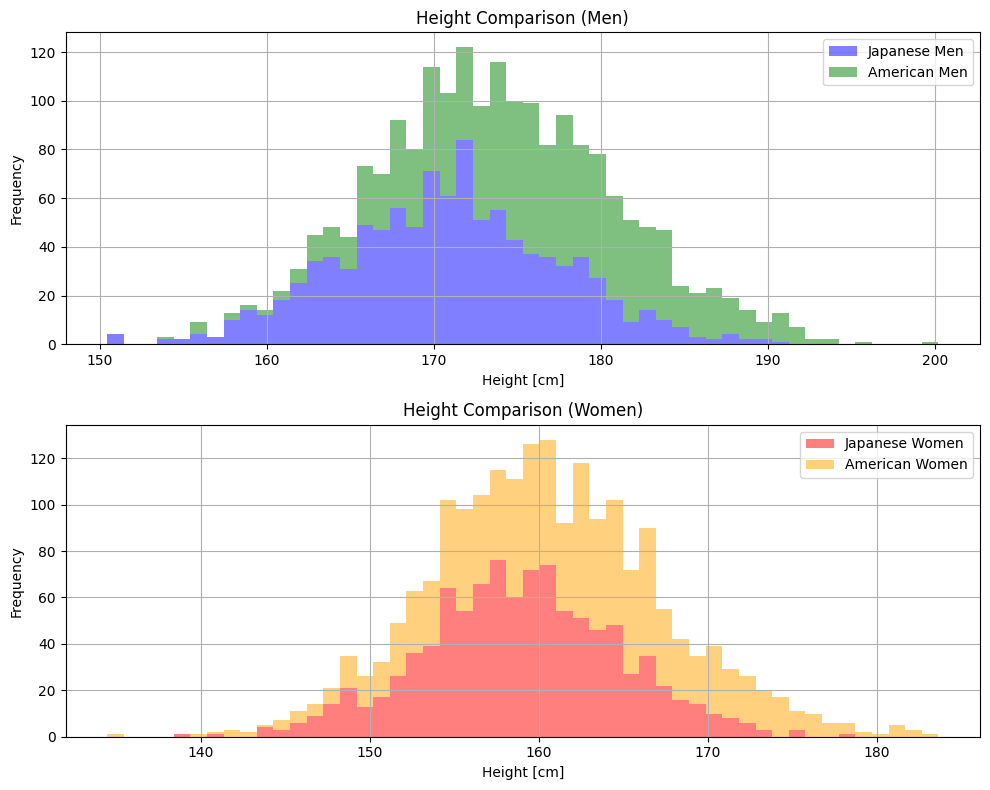
axs[0].hist([man, A_man], bins=50, color=['blue', 'green'], alpha=0.5, label=['Japanese Men', 'American Men'], stacked=True)
あい
一つの場所に
二つのデータが
入っていますね!